
GERD
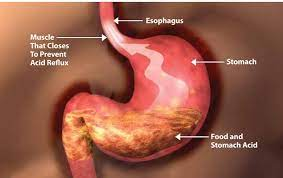
Definition: A condition wherein acidic contents from the stomach refluxes/regurgitates in the opposite direction into esophagus, oral cavity and/or lungs.
Gastro-esophageal reflux disease, also known as the reflux disease is one of the most commonly seen problems in the general population.
High risk groups:
Reflux disease is more common in:
- Elderly population (Age >60 years),
- Pregnant females,
- In overweight and obese patients,
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Consuming alcohol
- Tabacco smokers and chewers
Symptoms:
Common symptoms are burning sensation in your chest and regurgitation of food in mouth. Other common symptoms are abdominal discomfort, cough, excessive watering in mouth, sense of vomiting, recurrent dental carries and dental infection, dry cough.
Diagnosis:
Usually by typical history of symptoms. Some patients may require additional tests to rule out other serious mimickers.
Role of endoscopy:
To be done in patients who have failed to respond to medical therapy. A diagnostic upper GI scopy can be done as an outpatient basis and patients can be discharged within 1-2 hours of scopy.
Treatment:
Includes lifestyle change and pharmacotherapy.
Affected person should actively reduce his weight, exercise regularly, avoid harmful habits like smoking, alcohol and tobacco, should takeup more active lifestyle.
Avoid taking night time snacks, avoid taking heavy and fatty meals in one go, keep few hours gap between food and sleep and raise head end of bed while sleeping.
If all these lifestyle measures are not adequate, then patients should take drug treatment as prescribed by their doctor.
Refractory cases can be dealt with endoscopic therapeutic procedures.
